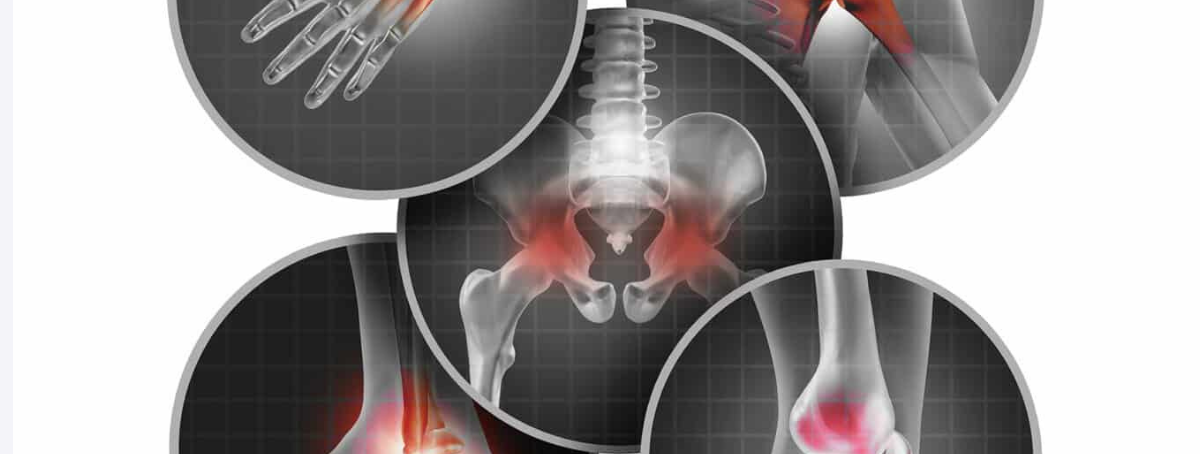
Cartilage is a crucial component of our musculoskeletal system, often overlooked until it starts to cause problems. This resilient, flexible tissue acts as a cushion between bones, allowing for smooth movement and protecting our joints from the daily wear and tear of life. However, as we age or due to various factors, cartilage can deteriorate, leading to a cascade of mobility issues and potential health complications. In this blog post, we’ll explore the intricacies of cartilage wear and tear, its impact on mobility, and the surprising health conditions that can arise when our ability to move freely is compromised.
Understanding Cartilage Wear and Tear
Cartilage wear and tear, also known as osteoarthritis when it affects joints, is a gradual process that occurs over time. Several factors can contribute to this breakdown:
1. Aging: As we get older, our body’s ability to repair and regenerate cartilage diminishes.
2. Repetitive stress: Certain occupations or activities that put constant stress on specific joints can accelerate wear.
3. Injuries: Trauma to joints can damage cartilage and lead to faster deterioration.
4. Obesity: Excess weight puts additional stress on weight-bearing joints.
5. Genetics: Some people are more predisposed to cartilage breakdown due to their genetic makeup.
As cartilage wears away, the bones in our joints begin to rub against each other, causing pain, stiffness, and inflammation. This process can affect any joint in the body but is most common in the knees, hips, hands, and spine.
The Impact on Mobility
The deterioration of cartilage can have a significant impact on our ability to move freely and comfortably. Here are some ways in which cartilage wear and tear affects mobility:
1. Joint Pain: As the cushioning effect of cartilage diminishes, movement becomes painful, discouraging physical activity.
2. Stiffness: Joints may become less flexible, making it harder to perform everyday tasks.
3. Reduced Range of Motion: As the condition progresses, the affected joints may not move as freely as before.
4. Instability: Worn cartilage can lead to joint instability, increasing the risk of falls and injuries.
5. Muscle Weakness: Pain and reduced movement can lead to muscle atrophy around the affected joints.
These mobility issues can significantly impact quality of life, making it challenging to perform daily activities, engage in hobbies, or maintain an active lifestyle. However, the consequences of reduced mobility extend far beyond just physical discomfort.
Health Conditions Arising from Reduced Mobility
When our ability to move freely is compromised, it can lead to a variety of health conditions that might not seem immediately related to cartilage wear and tear. Here are some potential health issues that can arise:
1. Cardiovascular Disease: Reduced physical activity can lead to poor cardiovascular health, increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke.
2. Obesity: Lack of movement often results in weight gain, which can exacerbate cartilage wear and tear and lead to other health problems.
3. Type 2 Diabetes: Regular physical activity helps regulate blood sugar levels. Reduced mobility can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
4. Osteoporosis: Weight-bearing exercises are crucial for maintaining bone density. Limited mobility can lead to bone loss and increased fracture risk.
5. Mental Health Issues: Chronic pain and reduced ability to engage in enjoyable activities can contribute to depression and anxiety.
6. Cognitive Decline: Physical activity is linked to better cognitive function. Reduced mobility may accelerate cognitive decline in older adults.
7. Digestive Issues: A sedentary lifestyle can lead to constipation and other digestive problems.
8. Respiratory Problems: Lack of movement can lead to shallow breathing and reduced lung capacity, increasing the risk of respiratory infections.
9. Sleep Disorders: Chronic pain and lack of physical activity can disrupt sleep patterns, leading to insomnia or sleep apnea.
10. Weakened Immune System: Regular exercise helps boost the immune system. Reduced mobility can lead to a higher susceptibility to infections.
Breaking the Cycle: Managing Cartilage Wear and Tear
While cartilage wear and tear is a natural part of aging, there are steps we can take to slow its progression and maintain our mobility:
1. Low-Impact Exercise: Activities like swimming, cycling, or tai chi can help maintain joint flexibility without putting excessive stress on cartilage.
2. Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight reduces stress on weight-bearing joints.
3. Proper Nutrition: A diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods and supplements like glucosamine and chondroitin may help support cartilage health.
4. Physical Therapy: Targeted exercises can strengthen the muscles around affected joints, improving stability and reducing pain.
5. Assistive Devices: Using canes, walkers, or orthotics can help reduce stress on affected joints during daily activities.
6. Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain relievers, topical treatments, or prescription medications can help manage pain and inflammation.
7. Lifestyle Modifications: Adapting your environment and daily routines can help reduce stress on affected joints.
8. Regular Check-ups: Consulting with healthcare professionals can help monitor the progression of cartilage wear and tear and adjust treatment plans as needed.
## Conclusion
Cartilage wear and tear is more than just a minor inconvenience or an inevitable part of aging. Its impact on mobility can have far-reaching effects on our overall health and well-being. By understanding the importance of cartilage health and taking proactive steps to maintain it, we can preserve our mobility and reduce the risk of developing associated health conditions.
Remember, it’s never too late to start taking care of your joints. Whether you’re young and looking to prevent future issues or already experiencing the effects of cartilage wear and tear, there are always steps you can take to improve your mobility and overall health. Consult with healthcare professionals to develop a personalized plan that addresses your specific needs and helps you maintain an active, healthy lifestyle for years to come.